At Ehisen, we specialize in advanced coating solutions for titanium anodes, using precisely formulated precious metal solutions. With patented coating technology and a strong R&D capability, we continually optimize coating formulas based on customer feedback, helping to significantly reduce procurement costs. Our titanium anodes, including Iridium-Tantalum, Ruthenium-Iridium, Platinum-Coated, and MMO (Mixed Metal Oxide) anodes, offer exceptional durability, catalytic efficiency, and operational stability. These products are widely used in industries such as hydrogen production, electroplating, water treatment, and cathodic protection. We work closely with customers to advance coating technologies, delivering cost-effective and reliable electrochemical solutions.

The MMO disc anode is a specialized cathodic protection device designed for optimal corrosion resistance. It features a disc shape and is reinforced with a mixed metal oxide coating that delivers a controlled electrical current to protect adjacent metal infrastructure. Mainly used in marine, oil and gas fields, its main application is to protect ships. This ensures asset longevity and operational efficiency, making it an indispensable tool for industry professionals.

MMO anode wire is mainly used for the production of flexible anodes, cathodic protection of pipeline interiors, and cathodic protection of water heater tanks. Flexible anodes are widely used as auxiliary anodes in impressed current cathodic protection systems for buried pipelines, storage tanks, and other buried metal structures. Titanium anode wire for water heaters is primarily used for the cathodic protection of water heater tanks and is the next-generation anode product replacing the sacrificial anode "magnesium rod."

MMO Titanium Probe Anodes consist of a titanium rod coated with a mixed metal oxide or platinum coating. The probe anode can withstand water turbulence without damage, the coating is not affected by sudden current reversals, and can be exposed to high current overloads for initial structural polarization without damage to the anode. They have been found to be resistant to acid attack and provide excellent protection in fresh, salt or salt water. They are available in a variety of sizes and configurations.

MMO tubular anodes are a corrosion protection device used in a variety of industries. It is a tubular structure coated with a durable MMO, usually iridium tantalum (IrO2 / Ta2O5) or iridium ruthenium (IrO2 / RuO2). Their purpose is to prevent corrosion of metal structures such as pipes, tanks and bridges by creating a rust-proof electrochemical reaction, thus extending the service life of equipment. They are known for their durability, low maintenance requirements and cost-effectiveness. They are critical to protecting critical infrastructure.

At Ehisen, we specialize in optimizing the precious metal coatings of titanium anodes to meet your specific needs. Here’s how we bring value to your projects:
Our technical team, led by Ph.D. graduates in electrochemistry from Japan's Tohoku University, possesses cutting-edge research and development capabilities. This ensures that every coating we design meets the highest standards of performance and reliability.
Collaborating with a diverse range of domestic and international clients, we refine coating ratios and additives to maximize performance. Many customers have already provided positive feedback on how our custom solutions enhanced their operations.
By analyzing your specific requirements, we calculate the most suitable coating composition and identify the ideal additives to enhance your anode’s functionality. This ensures precision in every solution we deliver.




Technical Director of Ehisen




CEO of Ehisen
Partnering with prestigious Chinese universities, we actively participate in research projects and leverage advanced laboratory equipment to validate and improve our coatings. This synergy allows us to push the boundaries of innovation and deliver state-of-the-art solutions.
We offer precious metal recycling services, extracting valuable materials from used titanium anodes. This capability allows us to produce cost-effective coatings for environments with less stringent performance requirements, reducing costs while promoting sustainability.
As active participants in titanium industry alliances, we attend regular summits and forums to stay informed of the latest industry trends. This enables us to remain at the forefront of innovation and share valuable insights with our clients.
Cathodic protection (CP) is essential because corrosion silently destroys metal infrastructure, leading to costly failures, environmental hazards, and safety risks. By using titanium anodes in impressed current CP systems, structures like pipelines, ships, and storage tanks are actively shielded from rust and degradation. This not only extends asset lifespans by decades but also prevents catastrophic leaks, reduces maintenance expenses, and ensures compliance with safety regulations—delivering a return on investment far greater than the cost of protection.

| Outer Diameter (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Length (mm) | Surface Area (㎡) | Current Output (mA/m) | Lifespan (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 16 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.05 | 5 | 20-30 |
| 16 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.05 | 30 | 20-30 |
| 19 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.06 | 6 | 20-30 |
| 19 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.06 | 36 | 20-30 |
| 25 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.08 | 8 | 20-30 |
| 25 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.08 | 48 | 20-30 |
| 32 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.1 | 10 | 20-30 |
| 32 | 1.0 | 1000 | 0.1 | 60 | 20-30 |
Other specifications and sizes can be customized according to customer requirements.
| Element | Iron (Fe) | Carbon (C) | Nitrogen (N) | Hydrogen (H) | Oxygen (O) | Titanium (Ti) | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Content | 0.20% | 0.08% | 0.03% | 0.02% | 0.18% | Balance | 0.40% |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium-Aluminum | 1mol/L Na₂SO₄ | 10000 | 25±5 |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium-Manganese | 1mol/L H₂SO₄ | 20000 | 40±5 |

MMO anode wire is widely used in the production of flexible anodes and for the cathodic protection of pipeline interiors, buried pipelines, and storage tanks. Made from titanium with a mixed metal oxide (MMO) coating, this titanium anode wire offers excellent corrosion resistance and long service life in impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) systems.
For water heater applications, MMO titanium anode wire provides reliable cathodic protection and serves as a durable alternative to the traditional sacrificial magnesium rod, offering longer lifespan and reduced maintenance.
| Diameter (mm) | Length (m) | Current Output (mA/m) | Lifespan (years) | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| φ1.0 | >100/roll | 15-100 | 20-40 | Storage tanks, gas stations |
| φ1.5 | >100/roll | 15-100 | 20-40 | Storage tanks, gas stations |
| φ2.0 | >100/roll | 15-100 | 20-40 | Storage tanks, gas stations |
| φ3.0 | >100/roll | 15-100 | 20-40 | Storage tanks, gas stations |
| Chemical Composition | Iron (Fe) | Carbon (C) | Nitrogen (N) | Hydrogen (H) | Oxygen (O) | Titanium (Ti) | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Content | 0.20% | 0.08% | 0.03% | 0.02% | 0.18% | Balance | 0.40% |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium-Tantalum | 1mol/L Na₂SO₄ | 10000 | 25 ± 5 |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ruthenium-Titanium | 1mol/L H₂SO₄ | 20000 | 40 ± 5 |

| Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Length L (m) | Current Output (mA/m) | Lifespan (years) | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6.35 | 0.635 | 152 | 17 | 20-50 | Storage tanks |
| 6.35 | 0.635 | 152 | 34 | 20-50 | Storage tanks |
| 6.35 | 0.635 | 152 | 43 | 20-50 | Storage tanks |
| 12.7 | 0.9 | 152 | 86 | 20-50 | Storage tanks |
| Chemical Composition | Iron (Fe) | Carbon (C) | Nitrogen (N) | Hydrogen (H) | Oxygen (O) | Titanium (Ti) | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Content | 0.20% | 0.08% | 0.03% | 0.02% | 0.18% | Balance | 0.40% |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium-Aluminum | 1mol/L Na₂SO₄ | 10000 | 25±5 |

MMO Titanium Probe Anodes consist of a titanium rod coated with a mixed metal oxide (MMO) or platinum layer, combining the mechanical strength of titanium with excellent electrochemical performance. The probe anode is designed to withstand water turbulence and dynamic flow conditions without coating damage. It remains stable under sudden current reversals and can tolerate temporary high current overloads during initial polarization without affecting service life.
These titanium probe anodes offer strong resistance to acid attack and perform reliably in fresh water, brackish water, and seawater environments. Available in various sizes and configurations, they can be customized to meet specific cathodic protection requirements.
Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) | Surface Area (㎡) | Current Output (mA/m) | Lifespan (years) |
12 | 1000 | 0.04 | 4 | 20 |
12 | 1000 | 0.04 | 24 | 20 |
20 | 1000 | 0.06 | 6 | 20 |
20 | 1000 | 0.06 | 36 | 20 |
*Other specifications and sizes can be customized according to customer requirements.
Chemical Composition
| Element | Iron (Fe) | Carbon (C) | Nitrogen (N) | Hydrogen (H) | Oxygen (O) | Titanium (Ti) | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Content | 0.20% | 0.08% | 0.03% | 0.02% | 0.18% | Balance | 0.40% |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iridium-Tantalum | 1mol/L Na₂SO₄ | 10000 | 25±5 |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ruthenium-Iridium | 1mol/L H₂SO₄ | 20000 | 40±5 |

| Diameter (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Current Output (mA/m) | Lifespan (years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.0-5.0 | 5 | 20 |
| 270 | 2.0-5.0 | 35 | 20 |
| 320 | 2.0-5.0 | 49 | 20 |
| 458 | 2.0-5.0 | 99 | 20 |
*Other specifications and sizes can be customized according to customer requirements.
Chemical Composition
| Element | Iron (Fe) | Carbon (C) | Nitrogen (N) | Hydrogen (H) | Oxygen (O) | Titanium (Ti) | Others |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum Content | 0.20% | 0.08% | 0.03% | 0.02% | 0.18% | Balance | 0.40% |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Boron-Aluminum | 1mol/L Na₂SO₄ | 10000 | 25±5 |
| System | Medium | Current Density (A/m²) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ruthenium-Boron | 1mol/L H₂SO₄ | 20000 | 40±5 |
Titanium anodes are widely used in cathodic protection systems to prevent corrosion of metal structures. Here’s how they function in various applications:
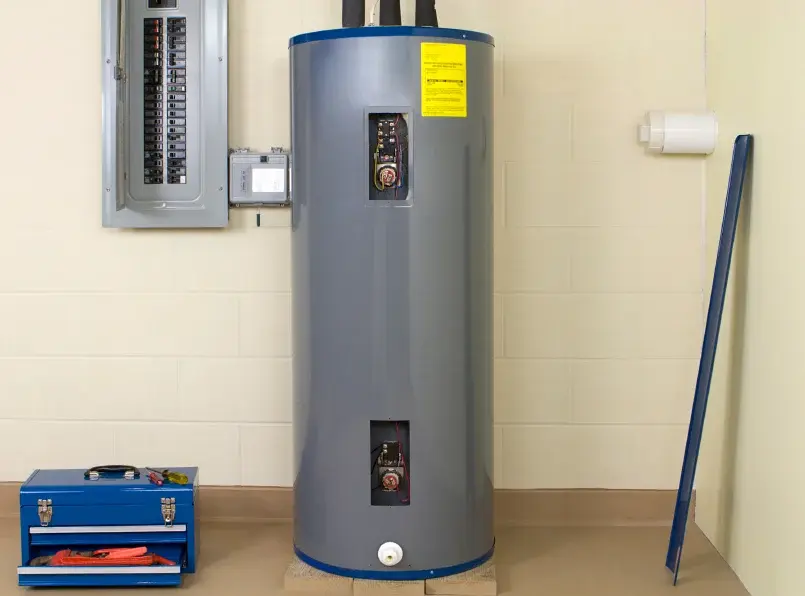

Titanium anodes are installed inside water heater tanks to protect the inner surfaces from corrosion.
They act as sacrificial anodes, corroding in place of the tank material (usually steel), thereby extending the lifespan of the tank.
The anodes are often coated with mixed metal oxides (MMO) to enhance their efficiency and durability in high-temperature and aggressive water environments.

In marine environments, titanium anodes are used to protect submerged structures such as ship hulls, offshore platforms, and docks.
They are connected to an impressed current cathodic protection (ICCP) system, where an external power source drives the anodes to release current, counteracting the corrosion process on the metal surfaces.
The anodes are particularly effective in seawater due to their high conductivity and resistance to chloride-induced corrosion.
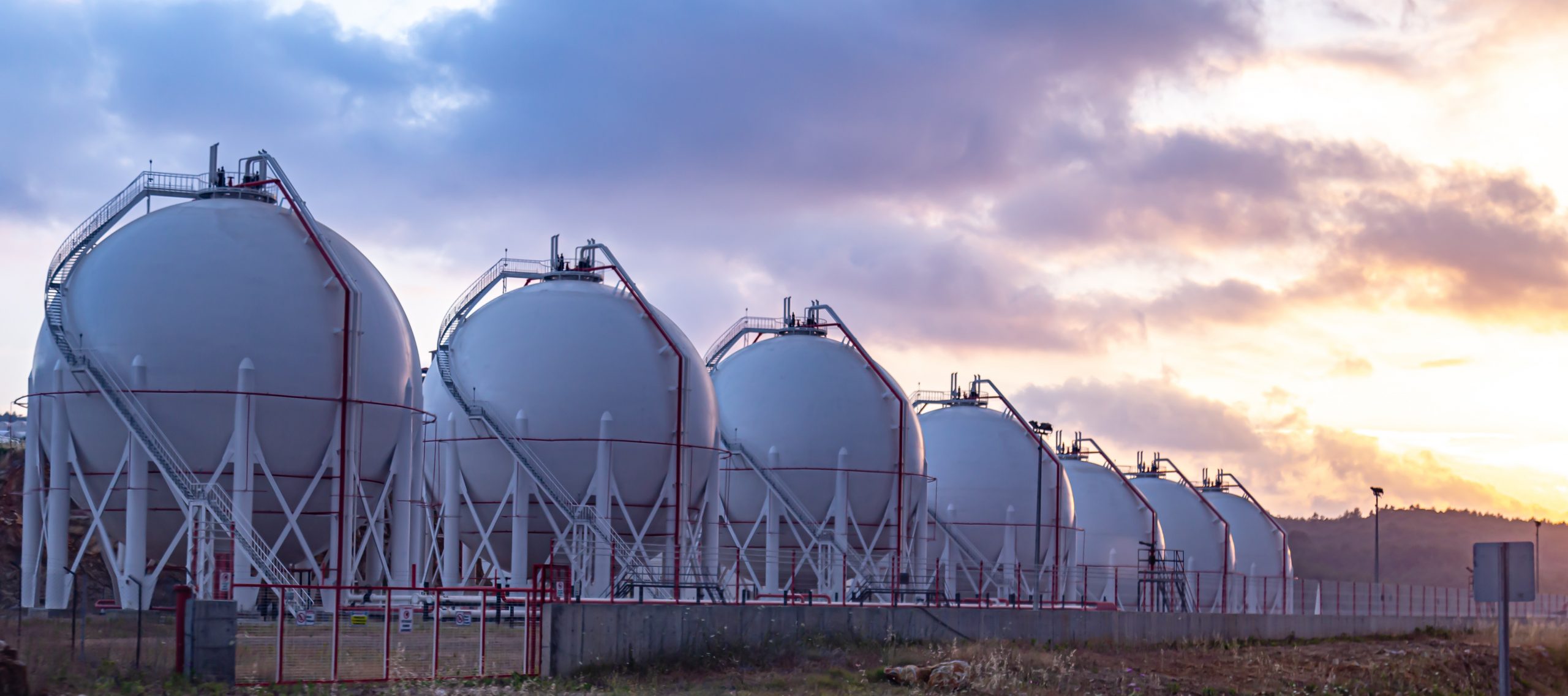

Inside oil storage tanks and pipelines, titanium anodes are used to protect against internal corrosion caused by aggressive fluids or gases.
In condensers and heat exchangers, the anodes prevent corrosion of metal surfaces exposed to cooling water or other corrosive media.
The anodes are often pre-packaged with conductive materials like coke breeze to ensure uniform current distribution and maximize protection.
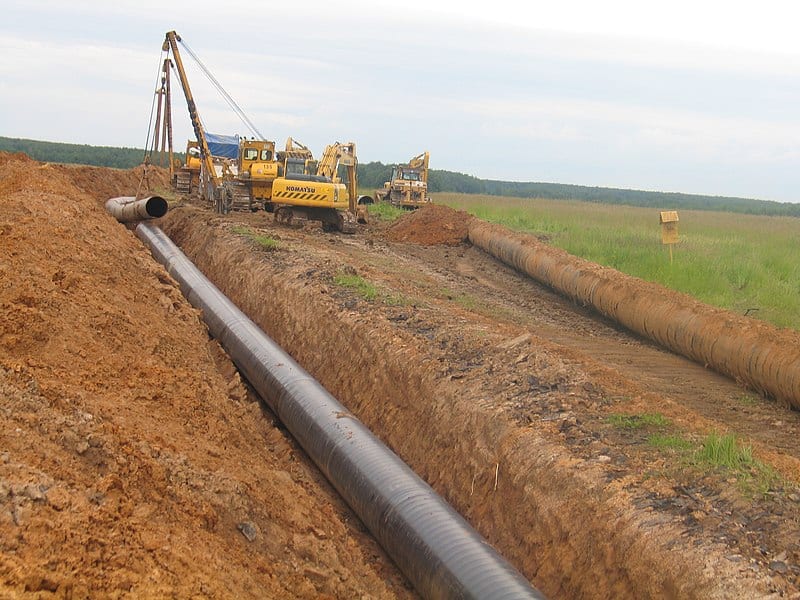

For buried structures such as pipelines or storage tanks, titanium anodes are installed in anode beds (shallow or deep) to provide cathodic protection.
The anodes are connected to an impressed current system, which generates a protective current that flows through the soil to the metal structure, preventing corrosion.
Titanium anodes are preferred in carbon-containing soils due to their high durability and resistance to chemical degradation.
In titanium cutting processes, preventing material damage and minimizing heat-affected zones (HAZ) are crucial for ensuring product quality. Below are some common issues encountered during cutting and their corresponding solutions:
High Corrosion Resistance: Titanium’s natural oxide layer makes it highly resistant to corrosion, even in aggressive environments.
Long Lifespan: Titanium anodes, especially those coated with MMO, have a significantly longer lifespan compared to traditional sacrificial anodes.
Efficiency: They provide consistent and reliable current output, ensuring effective protection over large areas.
Versatility: Titanium anodes can be customized in various shapes and sizes to suit specific applications, from small water heaters to large marine structures.
Select Appropriate Cutting Methods: Use non-thermal methods such as waterjet cutting or wire EDM to avoid HAZ.
Optimize Cutting Parameters: Lower cutting power and increase speed to reduce heat concentration.
Use Cooling Techniques: Introduce water or air cooling during cutting to lower surface temperatures.
Surface Protection Treatments: Apply anti-oxidation coatings before cutting to mitigate high-temperature oxidation.
Through external intervention, the entire metal surface becomes a cathode, eliminating the anodic zone and thus inhibiting the oxidative dissolution of the metal itself.
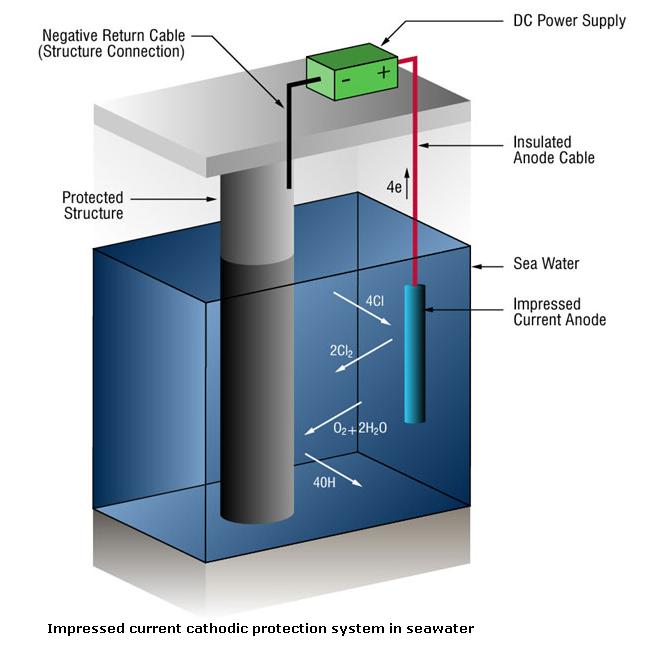
This diagram illustrates an Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP) system in seawater, where a DC power supply drives protective current through an MMO titanium anode to prevent corrosion of submerged steel structures.
In marine environments, chloride ions accelerate electrochemical corrosion. By installing a mixed metal oxide (MMO) coated titanium anode, the system introduces controlled direct current into the electrolyte (seawater), shifting the potential of the protected structure to a safe cathodic range. As a result, corrosion reactions on the steel surface are significantly reduced.
The titanium anode for cathodic protection is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply through an insulated anode cable, while the protected structure is connected to the negative terminal. The durable MMO coating enables long-term operation under high current density, strong salinity, and aggressive marine conditions, making it ideal for offshore platforms, seawater pipelines, storage tanks, and marine foundations.
Compared with sacrificial anodes, an impressed current titanium anode system offers:
Because of its corrosion resistance, dimensional stability, and excellent electrochemical performance, the MMO coated titanium anode has become the preferred solution for modern ICCP systems in seawater environments.
The more active metal is connected as the anode and is preferentially corroded. Relying on the potential difference between the two metals, so that the flow of electrons, the principle of the primary cell, the anode package as the positive

Potential: a physical quantity that describes the level of potential energy at a point in an electric field.
Potential difference: the difference in point position between two points in an electric field, creating a voltage.
Common Materials and Applications:Magnesium alloy (standard electrode potential: – 1.7 V): for fresh water, low salinity soils (e.g. underground pipelines).
Zinc alloy (- 1.1 V): for seawater environments (ships, steel piles at docks).
Aluminum alloy (- 0.8 to – 1.1 V): Less usage in comparison due to rapid consumption.
Principle of Sacrificial Anode Method:The more active metal is connected as the anode and is preferentially corroded. Relying on the potential difference between the two metals, electrons flow to form the principle of primary battery, with the anode package as the positive pole and the protected object as the negative pole, and electrons flow from the anode package to the protected object.
Characteristics of sacrificial anode method:No external power supply, low initial cost, but high long-term maintenance cost, need to replace the anode periodically.

Principle and composition: Through the constant potential meter, the current is output to the anode, and the current flows through the soil to the protected equipment.
Characteristics of the external current method: Continuous external power supply is required, high initial cost, but low long-term maintenance cost, regular inspection of the power supply and system is sufficient.
Applicable Scenarios: Applicable to large or continuous structures, such as long-distance pipelines, steel piles of wharves, etc., and can be adapted to high-resistivity environments.
| Comparison Dimension | Sacrificial Anode Method | Impressed Current Method |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Uses active metals (Zn, Mg, Al) to form a galvanic cell with the protected metal | External power source forces current to polarize the metal to a protective potential |
| Energy Dependency | No external power required | Requires continuous external power supply |
| Initial Cost | Low (only anode materials and installation) | High (requires power supply, auxiliary anodes, control systems) |
| Long-term Maintenance | High (periodic anode replacement) | Low (routine checks of power supply and systems) |
| Applicable Scale | Small or dispersed structures (e.g., ships, storage tanks) | Large or continuous structures (e.g., long-distance pipelines, harbor steel piles) |
| Environmental Suitability | Suitable for low-resistivity environments (seawater, humid soil) | Adaptable to high-resistivity environments (dry soil) |
| Current Adjustability | Fixed (depends on anode material properties) | Flexible (dynamic current intensity adjustment) |
| Service Life | Short (anode consumption: 1-5 years) | Long (auxiliary anode lifespan exceeds 20 years) |
Substrate: Pure titanium (e.g. Ta1, Ta2) is usually used as the substrate due to its excellent corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity and processability. Depending on the application scenario, the substrate can be made into plates, rods, meshes or other customized shapes.
Coatings: Coatings consist of mixed metal oxides, common oxides include: ruthenium oxide (Ru2O3), iridium oxide (Ir2O3), tantalum oxide (Ta2O₅), platinum oxide (PtO₂).

Performance Advantage: Combining the mechanical strength of titanium and the catalytic activity of oxide coating, the high catalytic activity surface significantly reduces the over-potential of electrode reaction and promotes the high efficiency of electrochemical reactions (e.g., precipitation of chlorine, precipitation of oxygen reaction).
| Metal Oxide | Chemical Formula | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applicable Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ruthenium Oxide | Ru₂O₃ | – High conductivity – Relatively low cost – Good electrochemical stability | – May undergo oxidative degradation under extreme conditions – Sensitive to certain media | – Widely used in seawater/freshwater environments – Low to medium current density applications |
| Iridium Oxide | Ir₂O₃ | – Extremely high electrochemical stability – Suitable for high current densities | – High cost – Limited resource availability | – Highly corrosive environments (e.g., strong acids/alkalis) – High current density requirements |
| Tantalum Oxide | Ta₂O₅ | – Excellent performance in strong acids – High electrochemical stability | – Low conductivity – High cost | – Strong acid environments (e.g., chemical industry) – Low current density scenarios |
| Platinum Oxide | PtO₂ | – Outstanding electrochemical performance – Suitable for high current densities | – High cost – Resource scarcity | – Demanding environments (e.g., deep-sea, high-salinity) – High current density requirements |

Ruthenium-iridium based formulations
High catalytic activity, suitable for the chlor-alkali industry Ratio: RuO₂ : IrO₂ : TiO₂ = 30-40% : 10-20% : 40-60% Sources: Patent US 4,422,917 (De Nora Corp.), The Electrocatalysis in the Chlorine Industry”.
Iridium- Tantalum based formulations
Corrosion resistant, suitable for seawater electrolysis Ratio: IrO₂ : Ta₂O₅ : SnO₂ = 20-30% : 50-60% : 10-20% Source: ISO 12474:2019 (Standard for Marine Cathodic Protection Anodes), Perma-Chem Technical Manual (2023 Edition)
Cleaning: Remove oil, oxidized skin and other impurities from the surface of titanium substrate.
Sandblasting: Increase surface roughness by sandblasting to improve coating adhesion.
Acid washing: Use acid solution (e.g. nitric acid-hydrofluoric acid) to further clean the surface and form an active surface.
Solution preparation: Select e.g. ruthenium chloride (RuCl₃), iridium chloride (IrCl₃), tantalum chloride (TaCl₅). Dissolve the precursor in a solvent (e.g., ethanol or isopropanol) to form a homogeneous coating solution. The solution concentration and composition ratio are adjusted as needed to optimize coating properties.
Coating application: The solution is uniformly applied to the surface of the titanium substrate by dipping, spraying or brushing, etc. The solution is dried at room temperature or low temperature, and the solvent is removed to form a uniform pre-coating.
Heat treatment: High temperature sintering: Heat treatment at high temperature (usually 400-600°C) to convert the coating into a stable metal oxide. Repeat coating and heat treatment as needed to ensure coating thickness and uniformity.
Growing Demand for Corrosion Prevention:The rapid development of infrastructure (e.g., bridges, pipelines, ports) and marine engineering (e.g., ships, offshore platforms) continues to increase the demand for efficient corrosion prevention technology.
2.Driven by environmental protection policies:The global emphasis on environmental protection and sustainable development has promoted the application of green technologies and materials.The application of MMO titanium anode in electrolysis industry (e.g. chlor-alkali industry) and water treatment meets the requirements of environmental protection and has great market potential.
3.Technological advancement:Continuous progress in coating technology and manufacturing process has enhanced the performance and application scope of MMO titanium anode. The research and development of new mixed metal oxide materials have further improved the conductivity and corrosion resistance of the anode.
4.Diversified Industry Demand:Increasing demand for high-performance anodes in oil & gas, chemical, electric power, metallurgy and other industries is driving the market expansion of MMO titanium anode.
Strengths:
Technology updates in downstream industries will expand demand.
Long life and low cost (long term).
Adaptable to a wide range of media (seawater, freshwater, soil) and complex environments for a wide range of applications.
Weaknesses
High technological threshold, complex coating preparation and heat treatment process, requiring high level of equipment and technical support.
Insufficient market awareness, some customers have insufficient understanding of the performance and advantages of MMO titanium anode.
Opportunities
Growing market demand: Rapid development of offshore engineering, oil and gas industry, infrastructure and other fields, the demand for high-performance anodes continues to increase. Emerging environmental protection technologies such as hydrogen production from electrolyzed water and sewage treatment provide new market opportunities for MMO titanium anodes. The global emphasis on environmental protection and sustainable development promotes the application of green materials.
1.Long Life & Low Maintenance Cost:MMO anode has long life and low maintenance cost, suitable for long term use.
2.High efficiency and energy saving: MMO anode reduces power loss by 20-30% compared with graphite anode, which meets the requirement of energy saving.
3.Adaptability to all scenarios:Applicable to various scenarios such as oil and gas industry, marine engineering, infrastructure field, new energy, etc., one material can be used for multiple purposes.
4.Environmental compliance: global carbon tax policy is tightened, MMO anode can be recycled although there is a risk of heavy metal leaching, and it complies with EU REACH and China RoHS standards.
Without proper cathodic protection (CP), metal structures face accelerated corrosion, leading to catastrophic failures, safety hazards, and massive financial losses. Here’s why CP is non-negotiable:
Pipelines/Bridges: Corrosion weakens structural integrity, increasing rupture risks.
Example: A 2022 study found 60% of pipeline leaks were corrosion-related (NACE International).
Marine Assets: Ship hulls and offshore platforms suffer pitting corrosion, risking oil spills or sinking.
Storage Tanks: Leaks contaminate soil/water (e.g., chemical leaks into groundwater).
Direct Costs: Replacing corroded assets is 5–10x more expensive than installing CP upfront.

Downtime: Unplanned shutdowns in oil/gas plants cost 500K–500K–1M per day (McKinsey).
Legal Fines: Non-compliance with corrosion standards (e.g., OSHA, EPA) leads to penalties.
Oil/chemical spills from corroded tanks/pipelines harm ecosystems and trigger lawsuits.
Case Study: The 2010 Kalamazoo River spill (USA) cost $1.2B to clean up due to pipeline corrosion.

Unprotected steel in seawater corrodes 100x faster (0.1 mm/year vs. 10 mm/year).
Concrete reinforcement bars (rebar) rust, causing cracks and collapse (e.g., bridge failures).
Year 1: Minor surface rust.
Year 5: Deep pitting, reduced load capacity.
Year 10: Catastrophic failure.
Titanium (Ti) is the preferred base material for high-performance impressed current anodes due to its unique physical and electrochemical properties. Here’s why:
Exceptional Corrosion Resistance

Forms a protective oxide layer (TiO₂) in air/water, preventing further degradation.
Resists pitting, crevice corrosion, and chloride attack (critical for seawater/acidic environments).
Unlike steel or copper, titanium does not dissolve under anodic polarization.
Lightweight & Mechanically Strong
Density: 4.5 g/cm³ (vs. steel’s 7.8 g/cm³), reducing structural load.
High strength-to-weight ratio, ideal for offshore/marine installations.
Biocompatibility & Stability
Non-toxic and inert, making it safe for potable water tanks and sensitive environments.
Excellent Electrical Conductivity (When Coated)
Pure titanium is a poor conductor, but MMO coating (e.g., IrO₂-Ta₂O₅) provides:
Low overpotential for oxygen evolution.
High current capacity (500–1,000 A/m²).
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Weight | Conductivity | Lifespan | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium (MMO-coated) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ (with coating) | 20–30+ years | ★★★★★ (long-term) |
| Graphite | ⭐⭐ (erodes in Cl⁻) | ⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | 5–10 years | ★★ (frequent replacement) |
| Platinum/Niobium | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ | 10–15 years | ★★ (extremely expensive) |
| Lead Alloys | ⭐⭐ (forms PbO₂ sludge) | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐ | 5–8 years | ★★★ (but toxic) |
| Steel | ⭐ (rusts rapidly) | ⭐⭐ | ⭐⭐⭐ | <2 years | ★ (high maintenance) |
Key Takeaways:
Titanium outperforms graphite/lead in harsh environments (e.g., seawater, high chloride).
More cost-effective than platinum for large-scale projects.
Eco-friendly compared to lead or cadmium-based anodes.
| Feature | Titanium MMO Anodes (ICCP) | Zinc/Magnesium (Galvanic) |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | External rectifier | Self-powered (sacrificial) |
| Lifespan | 20–30+ years | 1–5 years (consumable) |
| Current Output | Adjustable (high efficiency) | Limited (depends on environment) |
| Best For | Large structures (pipelines, ships) | Small, isolated assets |
Why ICCP with Ti Anodes?
✔ Precise control of protection potential (no over/under-protection).
✔ Ideal for high-resistivity environments (e.g., freshwater, concrete).
✔ Lower lifetime cost despite higher upfront investment.

Resists biofouling and chloride attack (vs. graphite, which degrades).
Used in desalination plants, ship hulls, and offshore rigs.
Stable in high-pH concrete (rebar CP) and corrosive soils.
Available as mesh, tubular, or wire anodes for flexible installation.
While other materials may seem cheaper upfront, titanium anodes offer unmatched durability, efficiency, and ROI for critical infrastructure.
CTA:
“Upgrade to titanium MMO anodes—contact our engineers for a free system design consultation.”
Selecting the optimal titanium anode for your cathodic protection (CP) system is crucial for long-term corrosion resistance, cost efficiency, and regulatory compliance. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you make the best choice based on your specific application.
A. Impressed Current Cathodic Protection (ICCP)
Uses externally powered titanium anodes (MMO-coated or platinized).
Best for:
Large structures (pipelines, ship hulls, storage tanks).
High-resistivity environments (soil, freshwater).
Systems requiring adjustable current output.
B. Galvanic (Sacrificial) Anodes
Uses active metals (Zn, Mg, Al) instead of titanium.
Best for:
Small, isolated structures.
Low-maintenance, low-cost solutions.
→ If you need ICCP, proceed to titanium anode selection.
A. Environment & Corrosivity
| Environment | Recommended Anode Type | Coating/Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Seawater | MMO-coated tubular/mesh | IrO₂-Ta₂O₅ (high Cl⁻ resistance) |
| Freshwater | Platinized titanium wire | Platinum layer (low overpotential) |
| Soil | MMO-coated rod/ribbon | Thick oxide coating (abrasion-resistant) |
| Concrete | MMO-coated ribbon/wire | Alkali-resistant formulation |
B. Current Density Requirements
Low current (10–100 A/m²): Thin MMO coating (5–10 µm).
High current (500–1000 A/m²): Thick MMO coating (15–20 µm) or platinized anodes.
C. Anode Shape & Installation
| Shape | Best For | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Mesh/Plate | Tank bottoms, large surfaces | Even current distribution |
| Tubular/Rod | Deep wells, pipelines | High mechanical strength |
| Wire/Ribbon | Rebar, concrete structures | Flexible, easy to install |
| Disc/Button | Localized protection | Compact, high precision |
D. Lifespan & Maintenance
Standard MMO anodes: 15–20 years (seawater).
Enhanced MMO anodes: 25+ years (higher IrO₂ content).
Platinized titanium: 10–15 years (for low-voltage applications).
❌ Choosing the wrong coating (e.g., using IrO₂-Ta₂O₅ in sulfuric acid—switch to Pt).
❌ Underestimating current demand, leading to premature anode failure.
❌ Ignoring installation constraints (e.g., using rigid rods where flexible ribbons are needed).

At Ehisen, we engineer titanium anodes to match your exact requirements:
✔ Material Customization: Grade 1/2/7 titanium for different corrosion levels.
✔ Coating Optimization: MMO (IrO₂-Ta₂O₅, RuO₂) or platinum for harsh conditions.
✔ Shape Flexibility: Mesh, tubular, wire, or custom geometries.
✔ Testing & Certification: ISO 9001, ASTM, NACE compliance.
Example Projects:
Offshore Wind Farm: Custom MMO tubular anodes for seawater CP (30-year design life).
Water Treatment Plant: Ribbon anodes for concrete tank protection.
Still unsure? Answer these questions, and we’ll recommend the best anode:
What’s your environment? (seawater, soil, concrete, etc.)
What’s your current demand? (A/m²)
Preferred anode shape? (rod, mesh, wire, etc.)
Contact Ehisen today for a free technical consultation or request a custom anode quote.
In titanium anode production, precise cutting and welding processes are essential. They directly impact product performance and cost control. We understand the challenges you face, such as maintaining strict angle tolerances during sintering, ensuring consistent welding quality, and balancing production costs. Here’s how we provide tailored solutions to simplify these complex issues and make collaboration more efficient:
Grade 1 or Grade 2 Titanium (ASTM B265) is selected for its high purity, corrosion resistance, and weldability.
Form: Supplied as sheets (for mesh/plate anodes), rods (for tubular anodes), or wires (for ribbon anodes).
Different Anode Shapes & Fabrication Methods:

Laser/Plasma Cutting
Titanium sheets are cut into required dimensions (e.g., 1000×500 mm) using CNC-controlled laser/plasma cutting for precision.
Holes or expanded mesh patterns are cut if needed.
Edge Smoothing
Burrs are removed via mechanical grinding or chemical polishing to prevent coating defects.

Turning & Drilling
Solid titanium rods are turned on a lathe to achieve precise diameters (e.g., Ø12 mm, Ø25 mm).
For hollow tubular anodes, deep-hole drilling is used to create internal bores.
Surface Grooving (Optional)
Spiral grooves may be machined to increase surface area for coating adhesion.

Cold Drawing
Titanium wire is drawn through dies to reduce diameter (e.g., Ø3 mm → Ø1.5 mm).
Rolling (For Ribbon Anodes)
Wire is flattened into ribbon (e.g., 5 mm width × 1 mm thickness) using precision rollers.

Objective: Remove machining oils, fingerprints, and organic residues.
Process Details:
Method: Ultrasonic cleaning in alkaline solutions (e.g., 5–10% NaOH + surfactant at 50–70°C).
Time: 5–15 minutes (longer for complex shapes like tubular anodes).
Post-Cleaning: Rinse with deionized (DI) water to avoid contamination.
Variations by Anode Type:
| Anode Type | Degreasing Method | Temperature | Time | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh/Plate | Ultrasonic bath | 60°C | 10 min | Ensures full coverage of holes/edges. |
| Tubular/Rod | High-pressure spray + ultrasonic | 70°C | 15 min | Removes trapped oils in bores. |
| Wire/Ribbon | Continuous belt cleaning | 50°C | 5 min | Faster process for thin materials. |

Objective: Eliminate native TiO₂ layer and activate the titanium surface.
Process Details:
Solution: 10–20% HNO₃ + 1–3% HF (hydrofluoric acid accelerates etching).
Time: 1–5 minutes (over-etching causes pitting).
Temperature: Room temp (20–25°C) for controlled reaction.
Post-Pickling: Immediate DI water rinse + neutralization (e.g., 5% NaHCO₃).
Variations by Anode Type
| Anode Type | HNO₃-HF Concentration | Time | Special Handling |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh/Plate | 15% HNO₃ + 2% HF | 3 min | Agitation to ensure even etching. |
| Tubular/Rod | 10% HNO₃ + 1% HF | 5 min | Internal bore flushing required. |
| Wire/Ribbon | 20% HNO₃ + 3% HF | 1 min | Rapid dip to avoid over-thinning. |
Safety Note: HF requires PPE (gloves, face shield) and proper waste treatment.

Objective: Increase surface area for better coating adhesion.
Methods & Parameters:
A. Sandblasting
Media: Al₂O₃ grit (80–120 mesh).
Pressure: 2–4 bar (lower for thin wires, higher for plates).
Standoff Distance: 10–20 cm.
B. Electrochemical Etching
Solution: 10% Oxalic acid (H₂C₂O₄) or H₂SO₄-NaF.
Voltage: 5–10V DC, 1–3 minutes.
Anode-Cathode Setup: Titanium workpiece (anode) vs. Pt/Ti cathode.
Variations by Anode Type:
| Anode Type | Roughening Method | Parameters | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh/Plate | Sandblasting | 120 mesh Al₂O₃, 3 bar | Uniform coverage required. |
| Tubular/Rod | Electrochemical | 8V, 2 min in H₂SO₄-NaF | Ensures internal bore roughness. |
| Wire/Ribbon | Light sandblasting | 80 mesh, 2 bar | Avoid excessive material loss. |

Drying: Nitrogen blow-drying or oven-drying at 80°C (prevents re-oxidation).
Key Quality Checks After Surface Prep
Water Break Test (ASTM F22):
A clean surface should hold a continuous water film (no beading).
Surface Roughness (Ra) Measurement:
Target: 0.5–2.0 µm (measured via profilometer).
Comparison Table: Surface Prep by Anode Type
| Step | Mesh/Plate Anodes | Tubular/Rod Anodes | Wire/Ribbon Anodes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Degreasing | Ultrasonic, 60°C, 10 min | Spray + ultrasonic, 70°C, 15 min | Belt cleaning, 50°C, 5 min |
| Pickling | 15% HNO₃ + 2% HF, 3 min | 10% HNO₃ + 1% HF, 5 min | 20% HNO₃ + 3% HF, 1 min |
| Roughening | Sandblasting (120 mesh) | Electrochemical (8V) | Light sandblasting (80 mesh) |

Coating Solution Preparation
Precursor salts (e.g., IrCl₃, TaCl₅) dissolved in organic solvents (e.g., butanol).
Brush/Spray Coating
Solution is applied evenly via brushing, spraying, or dip-coating.
Thermal Decomposition
Heated in a muffle furnace (400–550°C) to decompose salts into oxides (e.g., IrO₂-Ta₂O₅).
Process repeated 5–10 times to achieve 5–20 µm coating thickness.

Annealing
Final heat treatment (500–600°C) to stabilize oxide layers.
Quality Inspection
Adhesion Test: Tape peeling (ASTM D3359).
Electrochemical Testing: Polarization resistance & accelerated lifespan testing.
Tubular Anodes: End caps welded for sealing; titanium leads (Ø6 mm) welded for connectivity.
Ribbon Anodes: Spot-welded to titanium support frames.

Visual Inspection
Coating uniformity (no cracks/blisters).
Electrical Testing
Resistance measurement (<0.1 Ω·cm for MMO-coated anodes).
Certification
Compliance with ISO 9001, ASTM F2381, NACE SP0169.

Mesh/Plate: Packed in plastic-lined wooden crates to prevent scratching.
Tubular/Rod: Foam-wrapped in PVC tubes.
Wire/Ribbon: Coiled on spools with desiccant.
✔ Precision Machining: Ensures dimensional accuracy for all anode types.
✔ Controlled Coating: Optimized IrO₂-Ta₂O₅ ratios for high current efficiency.
✔ Traceability: Batch numbers recorded for quality assuranc
“Need custom titanium anodes? Our OEM production line delivers high-performance MMO anodes tailored to your specs. [Request a Quote].“
At Ehisen, we understand that effective cathodic protection begins with superior titanium anodes. With decades of expertise in advanced materials and corrosion engineering, we manufacture premium MMO-coated and platinized titanium anodes that deliver unmatched durability and performance across industries—from offshore oil platforms to municipal water systems.
Our anodes stand out through:
✔ Precision Engineering – Optimized IrO₂-Ta₂O₅ coatings for maximum current efficiency
✔ Application-Specific Designs – Mesh, tubular, wire, and custom geometries
✔ Rigorous Quality Control – ISO 9001, ASTM, and NACE compliant production
✔ Long-Term Value – Anodes engineered to last 20+ years in harsh environments
Whether you need standard solutions or fully customized anodes, Ehisen combines cutting-edge technology with hands-on CP expertise to protect your critical assets.
Contact us today to discuss how our titanium anodes can solve your corrosion challenges—because infrastructure shouldn’t have an expiration date.
Why Ehisen?
• Proven Performance – Trusted by global energy and infrastructure leaders
• End-to-End Support – From system design to anode fabrication
• Sustainable Solutions – Reducing lifecycle costs through intelligent CP design
Finding a reliable processor of titanium products is essential to your business success, and Ehisen is here to be that partner.
Send us a message if you have any questions or request a quote. We will be back to you ASAP!